Education


- Why Are Black Widow Males So Destructive?
We often hear about animals where the males mate with multiple females. However, many animals have the opposite system, where a single female courts and mates many males. This type of mating system (polyandry) can lead to some pretty interesting...
- Iom Past Question With Answers For Mbbs Entrance Exam
See the most important entrance questions for mbbs ( medical) students :- 1. Immature proglotids of Taenia solium have: c) Vitelline follicles and shellgland but not glands d) Uterus but neither ovaries nor testes 2. Which one of the following insects...
- Entrance Exam Questions Of Class 11 (biology )
Question Option1 Option2 Option3 Option4 Answer Tapeworm has no digestive system because: it is a parasite it lives in intestine it doesn’t need food it absorbs its food from general body surface 4 Flatworms are devoid of: Circulatory...
- Frog Dissection
Background: As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid and fertilized in water. On the outside of the frog’s head are two external nares, or nostrils;...
- Erlanger, Joseph (1874-1965)
Erlanger is a US physiologist and educator who, in collaboration with Herbert Gasser, developed techniques for recording nerve impulses using a cathode ray oscilloscope. In 1944 they shared the Nobel Prize for physiology or medicine for demonstrating...
Education
Earthworm Disection
arthworm Dissection


Pictures: Modern Biology, HoltThe following is a classification of a species in the earthworm family Lumbricidae. This common species is Lumbricus terrestris also known as the night crawler or dew worm.
| Phylum - Class - Family - Genus - Species - | Annelida Oligochaeta Lumbricidae Lumbricus terrestris |
Objectives:
• Describe the appearance of various organs found in the earthworm.
• Name the organs that make up various systems of the earthworm.
• Describe the appearance of various organs found in the earthworm.
• Name the organs that make up various systems of the earthworm.
Materials:
Safety goggles, dissecting pins, gloves, forceps, lab apron, scissors, paper towel, scalpel, water, dissecting probe, preserved earthworm, hand lens, dissection tray.
Safety goggles, dissecting pins, gloves, forceps, lab apron, scissors, paper towel, scalpel, water, dissecting probe, preserved earthworm, hand lens, dissection tray.
Purpose:
In this lab, you will dissect an earthworm in order to observe the external and internal structures of earthworm anatomy.
In this lab, you will dissect an earthworm in order to observe the external and internal structures of earthworm anatomy.
Background:
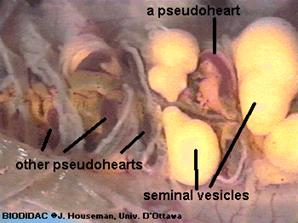
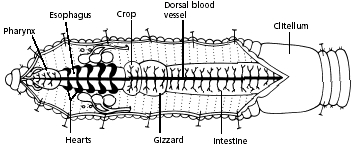
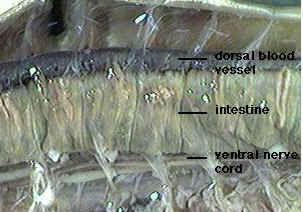
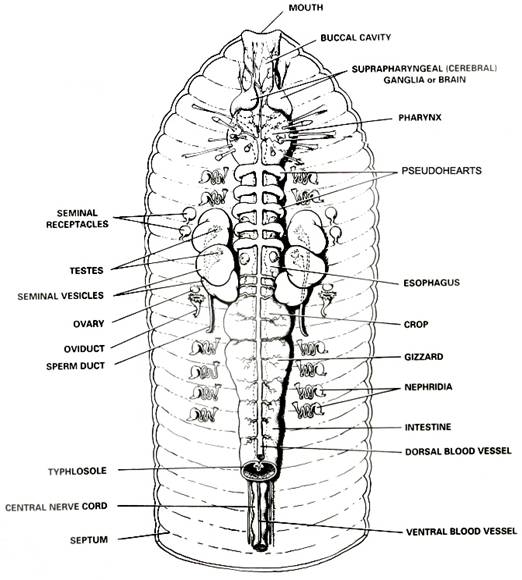
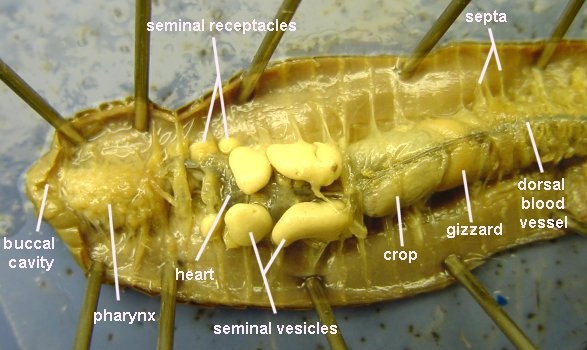
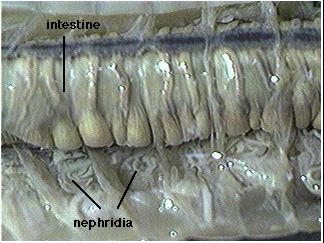
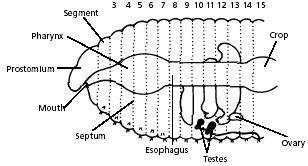
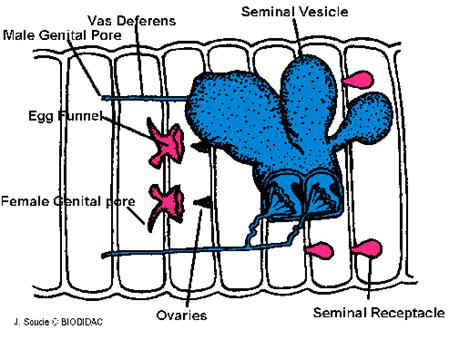
Among the most familiar invertebrate animals are the earthworms, members of the phylum Annelida. The word annelida means "ringed" and refers to a series of rings or segments that make up the bodies of the members of this phylum. Internally, septa, or dividing walls, are located between the segments. External segments are called metameres. There may be more than 100 segments in an adult worm. The clitellum is a swelling of the body found in sexually mature worms and is active in the formation of an egg capsule, or cocoon. Eggs are produced in the ovaries and pass out of the body through female genital pores. Sperm are produced in the testes and pass out through tiny male genital pores. During mating, sperm from one worm travel along the sperm grooves to the seminal receptacles of another worm. Fertilization of the eggs takes place outside the body as the cocoon moves forward over the body, picking up the eggs of one worm and the sperm of its mate. The pumping organs of the circulatory system are five aortic arches. Circulatory fluids travel from the arches through the ventral blood vessel to capillary beds in the body. The fluids then collect in the dorsal blood vessel and reenter the aortic arches. The earthworm takes in a mixture of soil and organic matter through its mouth, which is the beginning of the digestive tract. The mixture enters the pharynx, which is located in segments 1–6. The esophagus, in segments 6–13, acts as a passageway between the pharynx and the crop. The crop stores food temporarily. The mixture that the earthworm ingests is ground up in the gizzard. In the intestine, which extends over two-thirds of the body length, digestion and absorption take place. Soil particles and undigested organic matter pass out of the worm through the rectum and anus. The nervous system consists of the ventral nerve cord, which travels the length of the worm on the ventral side, and a series of ganglia, which are masses of tissue containing many nerve cells. The nerve collar surrounds the pharynx and consists of ganglia above and below the pharynx. Nervous impulses are responsible for movement and responses to stimuli. Each segment contains an enlargement, or ganglion, along the ventral nerve cord. Excretory functions are carried on by nephridia, which are found in pairs in each body segment. They appear as tiny white fibers on the dorsal body wall. The earthworm has no gills or lungs. Gases are exchanged between the circulatory system and the environment through the moist skin.
Among the most familiar invertebrate animals are the earthworms, members of the phylum Annelida. The word annelida means "ringed" and refers to a series of rings or segments that make up the bodies of the members of this phylum. Internally, septa, or dividing walls, are located between the segments. External segments are called metameres. There may be more than 100 segments in an adult worm. The clitellum is a swelling of the body found in sexually mature worms and is active in the formation of an egg capsule, or cocoon. Eggs are produced in the ovaries and pass out of the body through female genital pores. Sperm are produced in the testes and pass out through tiny male genital pores. During mating, sperm from one worm travel along the sperm grooves to the seminal receptacles of another worm. Fertilization of the eggs takes place outside the body as the cocoon moves forward over the body, picking up the eggs of one worm and the sperm of its mate. The pumping organs of the circulatory system are five aortic arches. Circulatory fluids travel from the arches through the ventral blood vessel to capillary beds in the body. The fluids then collect in the dorsal blood vessel and reenter the aortic arches. The earthworm takes in a mixture of soil and organic matter through its mouth, which is the beginning of the digestive tract. The mixture enters the pharynx, which is located in segments 1–6. The esophagus, in segments 6–13, acts as a passageway between the pharynx and the crop. The crop stores food temporarily. The mixture that the earthworm ingests is ground up in the gizzard. In the intestine, which extends over two-thirds of the body length, digestion and absorption take place. Soil particles and undigested organic matter pass out of the worm through the rectum and anus. The nervous system consists of the ventral nerve cord, which travels the length of the worm on the ventral side, and a series of ganglia, which are masses of tissue containing many nerve cells. The nerve collar surrounds the pharynx and consists of ganglia above and below the pharynx. Nervous impulses are responsible for movement and responses to stimuli. Each segment contains an enlargement, or ganglion, along the ventral nerve cord. Excretory functions are carried on by nephridia, which are found in pairs in each body segment. They appear as tiny white fibers on the dorsal body wall. The earthworm has no gills or lungs. Gases are exchanged between the circulatory system and the environment through the moist skin.

Procedure:
External Anatomy
1. Put on safety goggles, gloves, and a lab apron.
1. Put on safety goggles, gloves, and a lab apron.
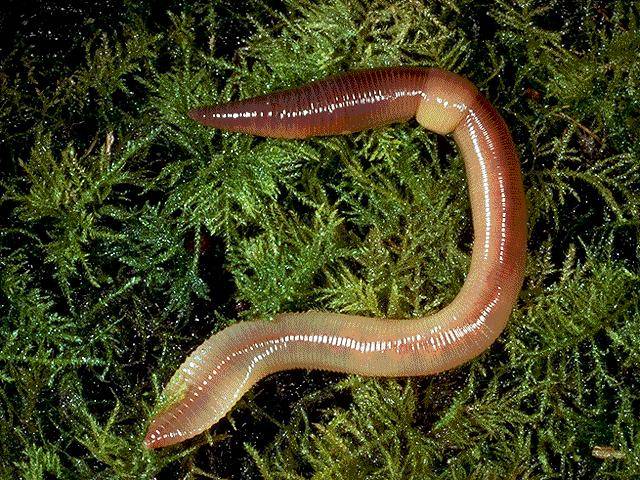
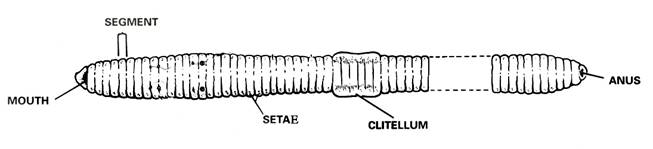
2. Place earthworm in the dissecting tray & rinse off the excess preservative. Identify the dorsal side, which is the worm’s rounded top, and the ventral side, which is its flattened bottom. Turn the worm ventral side up, as shown in the diagram below.

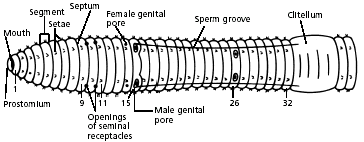
3. Use a hand lens as you observe all parts of the worm, externally and internally. Locate the conspicuous clitellum, a saddle-like swelling on the dorsal surface. The clitellum produces a mucus sheath used to surround the worms during mating and is responsible for making the cocoon within which fertilized eggs are deposited. The anterior of the animal is more cylindrical than the flattened posterior and is the closest to the clitellum. The ventral surface of the earthworm is usually a lighter colour than the dorsal surface. The mouth is located on the ventral surface of the first segment while the anus is found at the end of the last segment. Find the anterior end by locating the prostomium (lip), which is a fleshy lobe that extends over the mouth. The other end of the worm’s body is the posterior end, where the anus is located.

4. Locate the clitellum, which extends from segment 33 to segment 37. Look for the worm’s setae, which are the minute bristle-like spines located on every segment except the first and last one. Runyour fingers over the ventral surface of the earthworm’s body. You should be able to feel bristle-like setae used for locomotion
5. Refer again to the diagram of the ventral view of the worm to locate and identify the external parts of its reproductive system. Find the pair of sperm grooves that extend from the clitellum to about segment 15, where one pair of male genital pores is located. Look also for one pair of female genital pores on segment 14. There is another pair of male genital pores on about segment 26. Try to find the two pairs of openings of the seminal receptacles on segment 10. Note: These openings are not easy to see.
Internal Anatomy
Hint:Position your preserved earthworm dorsal side up and pin it down through the first segment and then again further back behind the clitellum. Cut a slit in the dorsal surface near the posterior pin. Using fine scissors extend the cut forward to the first segment. Be careful not to cut too deep. Starting at the first segment, cut the septa (thin membranes) that internally divide the segments, so the skin can be laid flat. Use additional pins to hold the integument open and expose the organs. Continue to lay the skin back until you have uncovered a centimeter or so of the intestine.
6. Turn the worm dorsal side up. Using a scalpel and scissors, make a shallow incision in the dorsal side of the clitellum at segment 33. CAUTION: Scalpels and scissors are very sharp. Report any cuts to your teacher. Using the forceps and scalpel, spread the incision open, little by little. Separate each septum from the central tube using a dissecting needle, and pin down each loosened bit of skin. Continue the incision forward to segment 1.
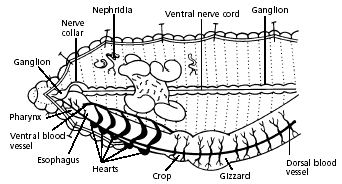
7. Use the diagram below to locate and identify the five pairs of aortic arches, or hearts. Then find the dorsal blood vessel. Look for smaller blood vessels that branch from the dorsal blood vessel.




Digestive System
The earthworm is an example of a foraging herbivorous annelid, obtaining food by eating its way through the soil and extracting nutrients from the soil as it passes through the digestive tract.
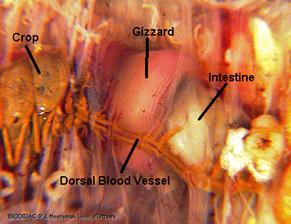
Hint: Starting at the anterior end, locate the muscular pharynx (food ingestion). This is followed by a tube-like esophagus which terminates in a crop (the wider organ) which serves as a storage stomach. Posterior to the crop you will find the gizzard. Gently press on the crop and gizzard to test their firmness. While the crop is soft and thin, the gizzard is muscular (soil is ground up and churned within the gizzard). The gizzard is followed by a long intestine in which both digestion and absorption occur. Undigested material is voided through the anus.
8. Locate the digestive tract, which lies below the dorsal blood vessel. Refer to the diagram above to locate the pharynx, esophagus, crop, gizzard, and intestine.

9. To find organs of the nervous system, push aside the digestive and circulatory system organs. Use the diagram below to locate the ventral nerve cord. Trace the nerve cord forward to the nerve collar, which circles the pharynx. Find one pair of ganglia under the pharynx and another pair of ganglia above the pharynx. The ganglia above the pharynx serve as the brain of the earthworm.


10. The worm’s excretory organs are tiny nephridia. There are two in every segment. Use the preceding diagram to locate some nephridia.

11. Use the diagram below to locate and identify a pair of ovaries in segment 13. Look for two pairs of tiny testes in segments 10 and 11. To find these organs, you will again have to push aside some parts already dissected.


12. Dispose of your materials according to the directions from your teacher.
13. Clean up your work area and wash your hands before leaving the lab.
You are given these worksheets as below:
Name(s)_______________________________ Group_______ Date__________ Period_______
| Earthworm Worksheet |  |
1. What is the name of the pumping organs of an earthworm?
2. Trace the parts of the digestive tract through which food passes.
3. Which parts of the earthworm serve as its brain? How are these parts connected to the rest of the body?
4. Which of the parts of the worm’s body that you saw are included in the excretory system?
5. How can you find out whether an earthworm eats soil?
6. Among the earthworm’s structural adaptations are its setae. How do you think the earthworm’s setae make it well adapted to its habitat?
7. How is the earthworm’s digestive system adapted for extracting relatively small amounts of food from large amounts of ingested soil?
8. Your dissection of the earthworm did not go beyond segment 32.What will you observe if you dissect the remainder of the worm to its posterior end?
9. On a separate piece of paper, draw and label the parts of the earthworm you observed, and color code the systems. Use green for the reproductive system, yellow for the digestive system, blue for the excretory system, and red for the nervous system.
10. During mating, two earthworms exchange sperm. Fertilization is external, and cocoons are produced from which the young eventually emerge. Refer again to steps 5 and 11, where you located the earthworm’s reproductive organs. Use a reference to identify the role of each organ in the reproductive process of the earthworm. On a separate paper, summarize your findings.
- Why Are Black Widow Males So Destructive?
We often hear about animals where the males mate with multiple females. However, many animals have the opposite system, where a single female courts and mates many males. This type of mating system (polyandry) can lead to some pretty interesting...
- Iom Past Question With Answers For Mbbs Entrance Exam
See the most important entrance questions for mbbs ( medical) students :- 1. Immature proglotids of Taenia solium have: c) Vitelline follicles and shellgland but not glands d) Uterus but neither ovaries nor testes 2. Which one of the following insects...
- Entrance Exam Questions Of Class 11 (biology )
Question Option1 Option2 Option3 Option4 Answer Tapeworm has no digestive system because: it is a parasite it lives in intestine it doesn’t need food it absorbs its food from general body surface 4 Flatworms are devoid of: Circulatory...
- Frog Dissection
Background: As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid and fertilized in water. On the outside of the frog’s head are two external nares, or nostrils;...
- Erlanger, Joseph (1874-1965)
Erlanger is a US physiologist and educator who, in collaboration with Herbert Gasser, developed techniques for recording nerve impulses using a cathode ray oscilloscope. In 1944 they shared the Nobel Prize for physiology or medicine for demonstrating...
