Education
- How Information Can Escape From A Black Hole?
Every black hole conceals a secret — the quantum remains of the star from which it formed, say a group of scientists, who also predict that these stars can later emerge once the black hole evaporates. The researchers call these objects "Planck...
- What Is Black Hole?
Black holes are some of the strangest and most fascinating objects found in outer space. They are objects of extreme density, with such strong gravitational attraction that even light cannot escape from their grasp if it comes near enough. Albert Einstein...
- Was Einstein The First To Invent E = Mc2?
In present world, no equation is more famous than E = mc2, and few are simpler. Indeed, the immortal equation’s fame rests largely on that utter simplicity: the energy E of a system is equal to its mass m multiplied by c2, the speed of light squared....
- Brief Biography Of Albert Einstein (1879-1955)
Albert Einstein is one of the greatest scientists of all times. He questioned widely accepted scientific truths and fine-tuned the scientific theories of Sir Isaac Newton. Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879 in Ulm, Wurttemberg, Germany. He studied...
- History Of The Black Hole Theory
A black hole in space has gravitational force so strong that nothing can escape from it, not even light. Hence no one can see a black hole astronomers are convinced they exist. John Michell, a British geologist and astronomer, designed the experiment...
Education
What Is General Relativity?
Theory Of General Relativity:-

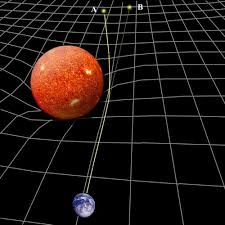
General relativity is a theory of gravitation developed by Einstein in the years 1907–1915. The development of general relativity began with the equivalence principle, under which the states of accelerated motion and being at rest in a gravitational field (for example when standing on the surface of the Earth) are physically identical. The upshot of this is that free fall is inertial motion: an object in free fall is falling because that is how objects move when there is no force being exerted on them, instead of this being due to the force of gravity as is the case in classical mechanics. This is incompatible with classical mechanics and special relativity because in those theories inertially moving objects cannot accelerate with respect to each other, but objects in free fall do so. To resolve this difficulty Einstein first proposed that space time is curved. In 1915, he devised the Einstein field equations which relate the curvature of space time with the mass, energy, and momentum within it.
Some of the consequences of general relativity are:
- Clocks run slower in deeper gravitational wells.This is called gravitational time dilation.
- Orbits process in a way unexpected in Newton's theory of gravity. (This has been observed in the orbit of Mercury and in binary pulsars).
- Rays of light bend in the presence of a gravitational field.
- Rotating masses "drag along" the spacetime around them; a phenomenon termed "frame-dragging".
- The universe is expanding, and the far parts of it are moving away from us faster than the speed of light.
Technically, general relativity is a theory of gravitation whose defining feature is its use of the Einstein field equations. The solutions of the field equations are metric tensors which define the topology of the space time and how objects move inertially.
SEE THEORY OF SPECIAL RELATIVITY HERE
SEE THEORY OF SPECIAL RELATIVITY HERE
- How Information Can Escape From A Black Hole?
Every black hole conceals a secret — the quantum remains of the star from which it formed, say a group of scientists, who also predict that these stars can later emerge once the black hole evaporates. The researchers call these objects "Planck...
- What Is Black Hole?
Black holes are some of the strangest and most fascinating objects found in outer space. They are objects of extreme density, with such strong gravitational attraction that even light cannot escape from their grasp if it comes near enough. Albert Einstein...
- Was Einstein The First To Invent E = Mc2?
In present world, no equation is more famous than E = mc2, and few are simpler. Indeed, the immortal equation’s fame rests largely on that utter simplicity: the energy E of a system is equal to its mass m multiplied by c2, the speed of light squared....
- Brief Biography Of Albert Einstein (1879-1955)
Albert Einstein is one of the greatest scientists of all times. He questioned widely accepted scientific truths and fine-tuned the scientific theories of Sir Isaac Newton. Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879 in Ulm, Wurttemberg, Germany. He studied...
- History Of The Black Hole Theory
A black hole in space has gravitational force so strong that nothing can escape from it, not even light. Hence no one can see a black hole astronomers are convinced they exist. John Michell, a British geologist and astronomer, designed the experiment...
