Education
- Was Einstein The First To Invent E = Mc2?
In present world, no equation is more famous than E = mc2, and few are simpler. Indeed, the immortal equation’s fame rests largely on that utter simplicity: the energy E of a system is equal to its mass m multiplied by c2, the speed of light squared....
- How Quantum Randomness Saves Relativity
In physics, Albert Einstein is famous for two things: developing the theory of relativity, and hating quantum mechanics. Relativity is a colossal achievement, with the special theory of 1905 putting classical physics on a firmer philosophical footing,...
- Doppler's Effects On Sound
Doppler's effects The apparent change in frequency of wave due to the relative motion between source and observer is called Doppler's effect.When source and observer move,there is change in velocity of wave.And when source moves towards observer,there...
- Brief Biography Of Albert Einstein (1879-1955)
Albert Einstein is one of the greatest scientists of all times. He questioned widely accepted scientific truths and fine-tuned the scientific theories of Sir Isaac Newton. Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879 in Ulm, Wurttemberg, Germany. He studied...
- History Of The Black Hole Theory
A black hole in space has gravitational force so strong that nothing can escape from it, not even light. Hence no one can see a black hole astronomers are convinced they exist. John Michell, a British geologist and astronomer, designed the experiment...
Education
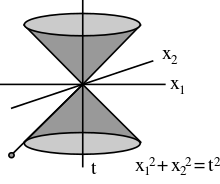
Theory Of Special Relativity
Einstein's Theory Of Special Relativity :-

Special relativity is a theory of the structure of space time. It was introduced in Einstein's 1905 paper "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies" . Special relativity is based on two postulates which are contradictory in classical mechanics:-
- The laws of physics are the same for all observers in uniform motion relative to one another (principle of relativity).
- The speed of light in a vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of their relative motion or of the motion of thelight source.
The resultant theory copes with experiment better than classical mechanics. For instance, postulate 2 explains the results of the Michelson–Morley experiment. Moreover, the theory has many surprising and counterintuitive consequences. Some of these are:
- Relativity of simultaneity: Two events, simultaneous for one observer, may not be simultaneous for another observer if the observers are in relative motion.
- Time dilation: Moving clocks are measured to tick more slowly than an observer's "stationary" clock.
- Relativistic mass
- Length contraction: Objects are measured to be shortened in the direction that they are moving with respect to the observer.
- Mass–energy equivalence: E = mc2, energy and mass are equivalent and transmutable.
- Maximum speed is finite: No physical object, message or field line can travel faster than the speed of light in a vacuum.
The defining feature of special relativity is the replacement of the Galilean transformations of classical mechanics by the Lorentz transformations.
SEE THEORY OF GENERAL RELATIVITY HERE
- Was Einstein The First To Invent E = Mc2?
In present world, no equation is more famous than E = mc2, and few are simpler. Indeed, the immortal equation’s fame rests largely on that utter simplicity: the energy E of a system is equal to its mass m multiplied by c2, the speed of light squared....
- How Quantum Randomness Saves Relativity
In physics, Albert Einstein is famous for two things: developing the theory of relativity, and hating quantum mechanics. Relativity is a colossal achievement, with the special theory of 1905 putting classical physics on a firmer philosophical footing,...
- Doppler's Effects On Sound
Doppler's effects The apparent change in frequency of wave due to the relative motion between source and observer is called Doppler's effect.When source and observer move,there is change in velocity of wave.And when source moves towards observer,there...
- Brief Biography Of Albert Einstein (1879-1955)
Albert Einstein is one of the greatest scientists of all times. He questioned widely accepted scientific truths and fine-tuned the scientific theories of Sir Isaac Newton. Albert Einstein was born on March 14, 1879 in Ulm, Wurttemberg, Germany. He studied...
- History Of The Black Hole Theory
A black hole in space has gravitational force so strong that nothing can escape from it, not even light. Hence no one can see a black hole astronomers are convinced they exist. John Michell, a British geologist and astronomer, designed the experiment...
